The parathyroid glands play an important role in regulating calcium and phosphorus levels in the body. Any disorder affecting these small glands can lead to an imbalance in mineral levels causing various health issues. This article discusses the symptoms, parathyroid causes, and treatment options for parathyroid disorders.
What are Parathyroid Disorders?
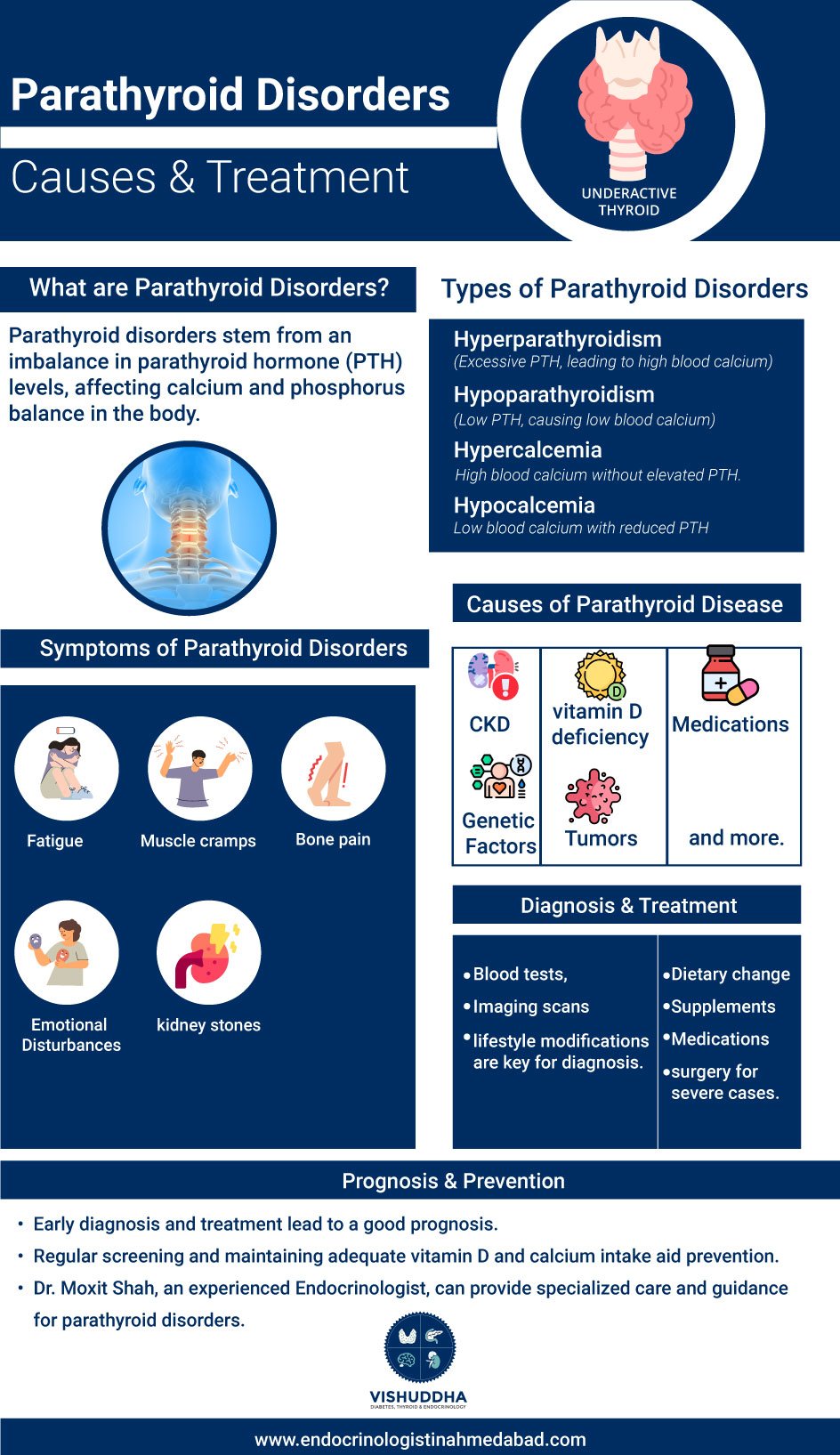
Parathyroid disorder refers to any condition that affects the normal function of the parathyroid gland. These glands, usually four, are located in or around the thyroid gland in the neck region. Their main function is to secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood. If PTH levels are too high or too low, it can upset the balance of this mineral and lead to a variety of health issues.
The parathyroid gland has the same name as the thyroid gland but for different purposes. The thyroid gland regulates metabolism, growth and development, the parathyroid gland specifically controls calcium and phosphorus homeostasis in the body.
What are Parathyroid Glands?
The parathyroid glands are four small endocrine glands located in or around the thyroid gland in the region of the neck Each parathyroid gland produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates the levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood work. Calcium is essential for various functions in the body such as bone formation, muscle contraction, circulation, etc. Phosphorus also plays an important role and maintains calcium to balance Parathyroid disease hormone regulates the absorption of calcium from food and saliva and helps the kidneys excrete phosphorus to maintain optimal levels of these minerals.
Types of Parathyroid Disorders
There are four main types of parathyroid disorders caused due to imbalance of PTH levels:
- Hyperparathyroidism: It occurs when there is excessive secretion of PTH from the parathyroid glands leading to high blood calcium levels. Primary hyperparathyroidism is commonly caused due to a benign tumor in the parathyroid gland.
- Hypoparathyroidism: In this condition, insufficient PTH is secreted causing abnormally low blood calcium and high phosphorus levels. It can be a result of damage to the parathyroid glands during thyroid surgery.
- Hypercalcemia: High levels of blood calcium without high PTH are called hypercalcemia. It can occur due to certain cancers that secrete PTH-related proteins.
- Hypocalcemia: Low calcium levels in the blood associated with low or absent PTH is termed as hypocalcemia. It is commonly seen in hypoparathyroidism.
Symptoms of Parathyroid Disorders
Not all conditions show obvious Parathyroid symptoms since the body tries to maintain normal mineral levels. Some common symptoms seen in parathyroid disorders are:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Numbness and tingling sensation
- Bone and joint pain
- Emotional disturbances
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Kidney stones
- Memory problems
Causes of Parathyroid Disease
The causes of parathyroid disorders can be:
- Chronic kidney disease
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Certain medications like lithium
- Endocrine disorders like hyperthyroidism
- Rarely cancer of the parathyroid gland
- Benign tumours of the parathyroid gland
- Enlarged parathyroid glands
- Genetic conditions affecting gland function
- Radiation exposure or neck injury
Diagnosis and Treatment of Parathyroid Conditions
Diagnosis involves blood tests to check calcium, phosphorus, and PTH levels. Ultrasound or sestamibi scan may be done to locate any tumours. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition:
- Lifestyle modifications such as dietary control and adequate calcium intake
- Vitamin D and other supplements
- Bisphosphonate drugs for bone strengthening
- Cinacalcet helps control calcium in hyperparathyroidism
- Parathyroidectomy surgery to remove the tumour in severe cases
- Calcitriol, a calcium supplement for hypocalcemia
- Dialysis for patients with renal failure
The mainstay for parathyroid treatment is that a single benign tumour raises calcium levels is parathyroidectomy. In this minimally invasive surgery, the tumour is removed along with the associated parathyroid glands. It aims to restore the normal mineral balance
Prognosis and Prevention
With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the prognosis is usually good for parathyroid disorders. Surgery provides a cure for primary hyperparathyroidism in over 90% cases. Regular screening of high-risk groups can aid early detection. Maintaining adequate vitamin D and calcium intake helps prevent secondary causes. Family screening is recommended if genetic conditions are suspected. Following treatment plans strictly helps prevent complications.
Conclusion
In summary, parathyroid disorders can develop due to various causes that disrupt the normal functioning of the parathyroid glands. This leads to an imbalance in calcium and phosphorus levels, resulting in a range of symptoms. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment tailored to the individual can help manage the condition effectively. If you want such adherence to treatment plans and monitoring you can contact Dr Moxit Shah, a renowned Endocrinologist who specialises in diagnosing and treating health conditions related to body hormones and different kinds of diabetes. Following medical advice regarding medication, diet, lifestyle, and surgery (if needed) is important for recovery and preventing long-term complications.