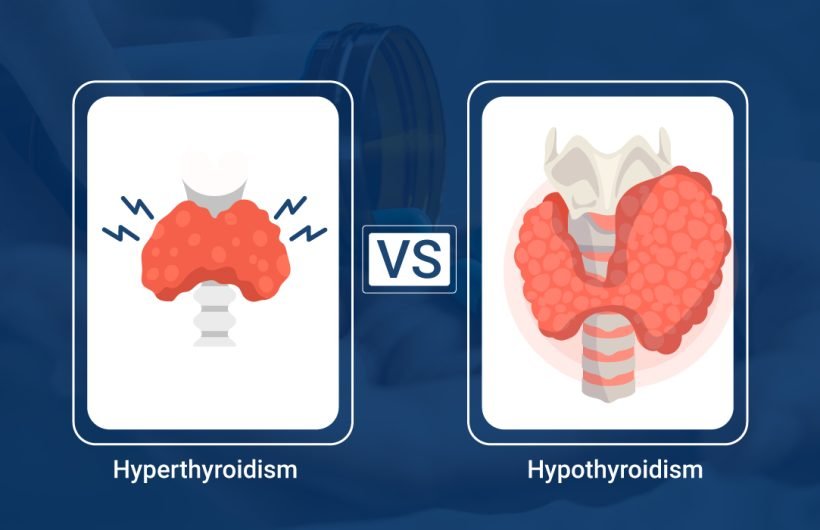
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall bodily functions. However, when the thyroid gland produces either too little or too much thyroid hormone, it can lead to two distinct medical conditions: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Although both conditions affect the thyroid gland, they have opposite effects on the body. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, including their symptoms, causes, and treatments. Understanding these conditions can help individuals recognize the signs and seek appropriate medical attention to manage their thyroid health.
What is the difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are two distinct medical conditions that affect the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism and other bodily functions.
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces an excess of thyroid hormone, which can result in an overactive metabolism. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, sweating, nervousness, and irritability.
On the other hand, hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormone, which can result in an underactive metabolism. Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include weight gain, fatigue, constipation, dry skin, and feeling cold.
Symptoms difference between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
The symptoms of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can vary widely and may be mistaken for other health issues. Here are some of the key symptoms that differentiate hypothyroidism from hyperthyroidism:
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Feeling cold
- Depression
- Slow heart rate
- Muscle aches and stiffness
- Menstrual irregularities
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
- Weight loss
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nervousness and anxiety
- Tremors in the hands or fingers
- Sweating and sensitivity to heat
- Difficulty sleeping
- Increased bowel movements
- Muscle weakness
- Changes in menstrual patterns
- Changes in vision or eye irritation
It’s important to note that not everyone with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism will experience all of these symptoms. In some cases, symptoms may be mild or may not appear at all. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider like Dr. Moxit Shah for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Cause the difference between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
The causes of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism differ, and they are related to the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
Causes of Hypothyroidism:
- Autoimmune diseases: The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disorder called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. This occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to damage and reduced thyroid hormone production.
- Radiation therapy: Exposure to radiation, such as during cancer treatment, can damage the thyroid gland and reduce its function.
- Thyroid surgery: Removal of the thyroid gland due to cancer or other conditions can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as lithium, amiodarone, and interferon, can interfere with thyroid hormone production and lead to hypothyroidism.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: Some babies are born with an underactive thyroid gland, which can result in hypothyroidism.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism:
- Graves’ disease: The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease. This occurs when the body’s immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to produce too much thyroid hormone.
- Thyroid nodules: Nodules or lumps that develop in the thyroid gland can produce excess thyroid hormone and cause hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland can cause excess thyroid hormone to be released into the bloodstream.
- Excessive iodine intake: Consuming too much iodine, either through diet or supplements, can cause hyperthyroidism.
- Pituitary gland malfunctions: Rarely, hyperthyroidism can be caused by a problem with the pituitary gland, which regulates the thyroid glands hormone production.
Overall, the causes of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can be complex and multifactorial. A healthcare provider like Dr. Moxit Shah can help determine the underlying cause of thyroid dysfunction and recommend appropriate treatment options.
How Are Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism Diagnosed and Treated?
To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, a healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination and order blood tests to measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. Additional tests, such as an ultrasound or thyroid scan, may be ordered to evaluate the size and function of the thyroid gland.
The treatment for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism differs based on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Treatment of Hypothyroidism:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy: The most common treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone orally to replace the missing hormone. This medication helps to restore normal hormone levels and improve symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications: In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular exercise can also help manage symptoms and support thyroid health.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism:
- Anti-thyroid medications: The most common treatment for hyperthyroidism is medication that reduces the amount of thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment involves taking a dose of radioactive iodine, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and destroys the overactive cells.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery to remove the thyroid gland may be recommended for severe or persistent hyperthyroidism.
In summary, the treatment for hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Healthcare providers can work with individuals to determine the best course of treatment and management strategies to support thyroid health.
Call to Action
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are two conditions that affect the thyroid gland and can have a significant impact on a person’s health and well-being. While hypothyroidism is characterized by an underactive thyroid gland and reduced thyroid hormone production, hyperthyroidism is marked by an overactive thyroid gland and excess thyroid hormone production. The symptoms, causes, and treatment options for these conditions can differ widely.
If you suspect you may have hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Dr. Moxit Shah is an endocrinologist who specializes in thyroid disorders and can provide expert guidance on managing these conditions. With proper treatment and management, individuals with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.