Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions of people worldwide, comes with numerous potential complications. Among these complications, diabetic eye disease stands out as a significant concern, posing risks to vision and overall ocular health. For those living with diabetes, understanding the complexities of diabetic eye disease is essential to preserving vision and preventing severe complications. In this blog, we will discuss the consequences of diabetic eye disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatments, and the crucial role of diabetic eye care specialists in managing this condition effectively.
What is Diabetic Eye Disease?
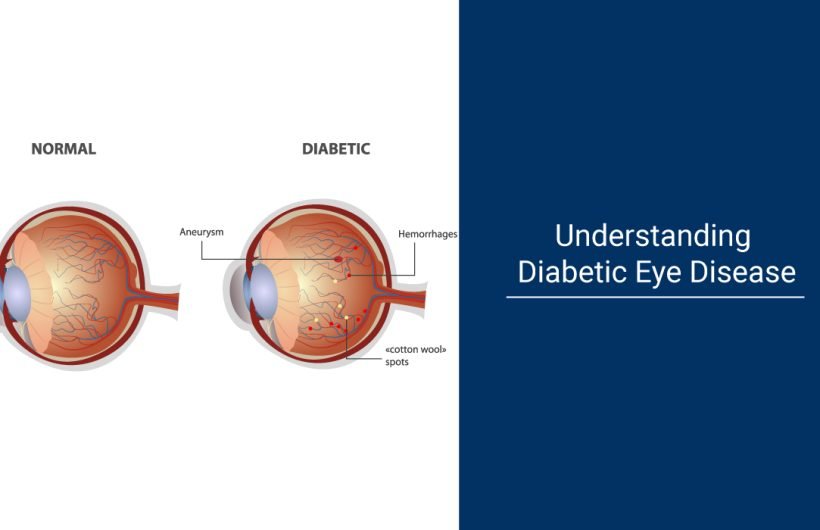
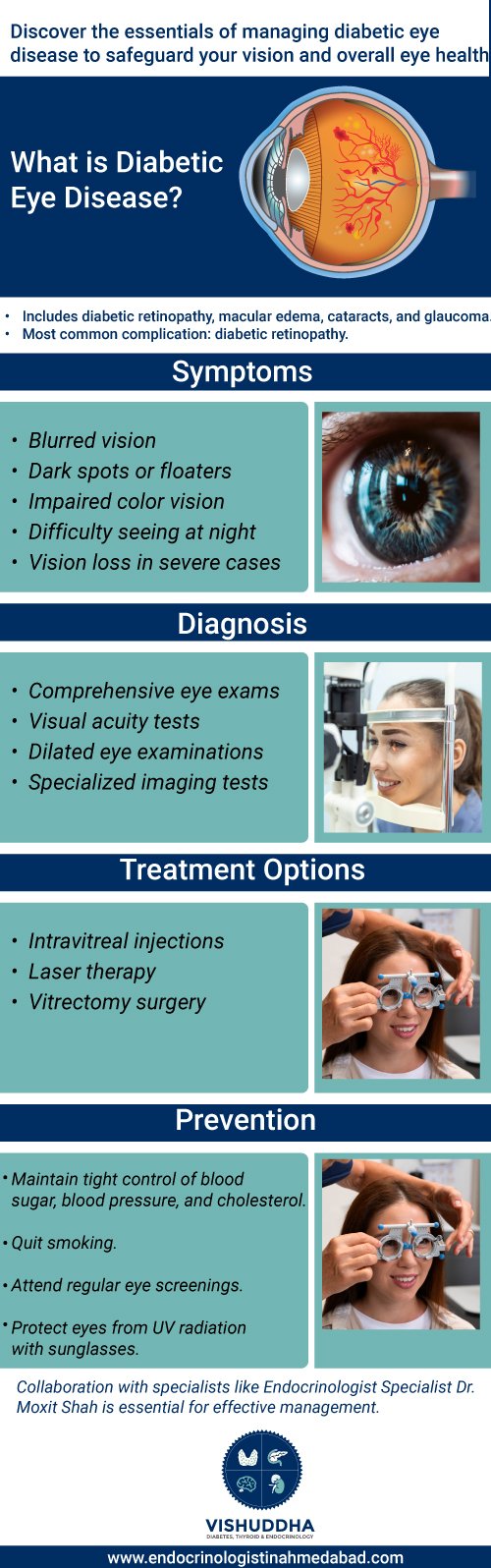
Diabetic eye disease encompasses a group of eye conditions that can affect individuals with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. Among these, diabetic retinopathy is the most common and potentially sight-threatening complication of diabetes.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. As the disease progresses, these blood vessels may leak fluid or bleed, causing vision problems and, in severe cases, leading to blindness.
Diabetic macular edema, a complication of diabetic retinopathy, involves swelling in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. This swelling can distort vision and, if left untreated, can result in permanent vision loss.
Cataracts, another common complication of diabetes, involve clouding of the eye’s natural lens, leading to blurry vision and eventual vision impairment if not addressed. Glaucoma, characterized by increased pressure within the eye, can also occur in individuals with diabetes, further complicating vision management.
Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Disease
One of the challenges with diabetic eye disease is that it often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may feel symptoms like :
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Dark spots or floaters in the field of vision
- Impaired color vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Vision loss or blindness in severe cases
Individuals with diabetes need to undergo regular eye exams, even in the absence of symptoms, to detect and manage diabetic eye disease promptly.
How Is Diabetic Eye Disease Diagnosed?
Diabetic eye disease is diagnosed through comprehensive eye exams, including visual acuity tests, dilated eye examinations, and specialized imaging tests like fluorescein angiography and optical coherence tomography (OCT). These tests help eye care specialists identify signs of diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, and other complications. Collaboration with other healthcare providers ensures optimal diabetes management to reduce the risk of vision loss. Early detection through regular screenings is vital for timely treatment and preservation of vision in individuals with diabetes.
Can Diabetic Eye Disease Be Reversed or Only Managed?
Diabetic eye disease is manageable but generally not reversible. With early detection and proper management, the progression of diabetic eye disease can be slowed or halted, and vision loss can be minimized. Treatment options such as intravitreal injections, laser therapy, and surgery may be employed to preserve vision and prevent further damage to the eyes. However, once damage to the retina or other structures occurs, it is often irreversible. Therefore, proactive management, including regular eye exams and optimal diabetes control, is essential to effectively manage diabetic eye disease and maintain vision for as long as possible.
Diabetic Eye Care Specialists
Given the complexities of diabetic eye disease, specialized care is crucial for effective management. Diabetic eye care specialists, including ophthalmologists and optometrists with expertise in treating eye conditions associated with diabetes, play a pivotal role in preserving vision and preventing complications.
These specialists possess the knowledge and skills required to diagnose and treat diabetic eye disease comprehensively. They conduct thorough eye exams, which may include dilated eye screenings to assess the retina and detect any signs of diabetic retinopathy or other complications.
In addition to regular eye exams, diabetic eye care specialists collaborate with other healthcare providers, including primary care physicians and endocrinologists, to optimize diabetes management. Tight control of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol is essential for reducing the risk of diabetic eye disease progression.
Treatment for Diabetic Eye Disease
The treatment approach for diabetic eye disease depends on the specific condition and its severity. Some common treatment options include:
- Intravitreal injections: Medications injected into the eye to reduce swelling and inflammation, particularly beneficial for diabetic macular edema.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatment, such as focal laser photocoagulation or panretinal photocoagulation, can help seal leaking blood vessels or shrink abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
- Vitrectomy: In advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy with significant bleeding or scar tissue formation, vitrectomy surgery may be necessary to remove blood and scar tissue from the eye’s vitreous gel.
These treatments aim to preserve vision, prevent further damage to the retina, and reduce the risk of blindness in individuals with diabetic eye disease.
Some ways to prevent diabetic eye diseases
While diabetic eye disease can be challenging to manage, several preventive measures and lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of complications:
- Maintain tight control of blood sugar levels through proper diabetes management, including medication adherence, healthy eating habits, and regular exercise.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol levels to minimize the risk of vascular complications affecting the eyes.
- Quit smoking, as smoking can exacerbate diabetic eye disease and increase the risk of vision loss.
- Attend regular eye screenings and follow-up appointments with diabetic eye care specialists, even in the absence of symptoms.
- Protect the eyes from ultraviolet (UV) radiation by wearing sunglasses outdoors, as UV exposure can accelerate cataract formation.
By adapting these habits and incorporating regular eye care into their diabetes management routine, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their vision and minimize the impact of diabetic eye disease.
conclusion
In conclusion, proactive management, and collaboration with skilled specialists like Dr. Moxit Shah are key to effectively managing diabetic eye disease and preserving vision. Dr. Moxit Shah’s expertise in diabetic eye care ensures comprehensive evaluations, personalized treatment plans, and compassionate care for individuals living with diabetes. By prioritizing regular eye exams and adhering to recommended treatment strategies, patients can take control of their eye health and reduce the risk of vision loss. With the Best Diabetes Doctor Dr. Moxit Shah’s guidance and expertise, individuals can navigate diabetic eye disease with confidence, knowing they are in capable hands.