Honey is often seen as a healthier option than white sugar because it is natural, rich in flavour, and contains small amounts of antioxidants. However, for people living with diabetes, an important question remains. Can diabetics eat honey safely?
The answer is not a simple yes or no. In this detailed guide, Diabetologist in Ahmedabad, Dr Moxit Shah, explains how honey affects blood sugar levels, the possible benefits and risks for people with diabetes, and how honey can be included carefully in a diabetes friendly diet.
Is Honey Safe for People with Diabetes?
Yes, people with diabetes can eat honey, but only in moderation and with careful planning. Even though honey is natural, it is still made mostly of sugar, mainly glucose and fructose, which can raise blood sugar levels.
One tablespoon of honey contains around seventeen grams of sugar and carbohydrates. These carbohydrates are quickly broken down into glucose, causing blood sugar to rise in a way similar to table sugar.
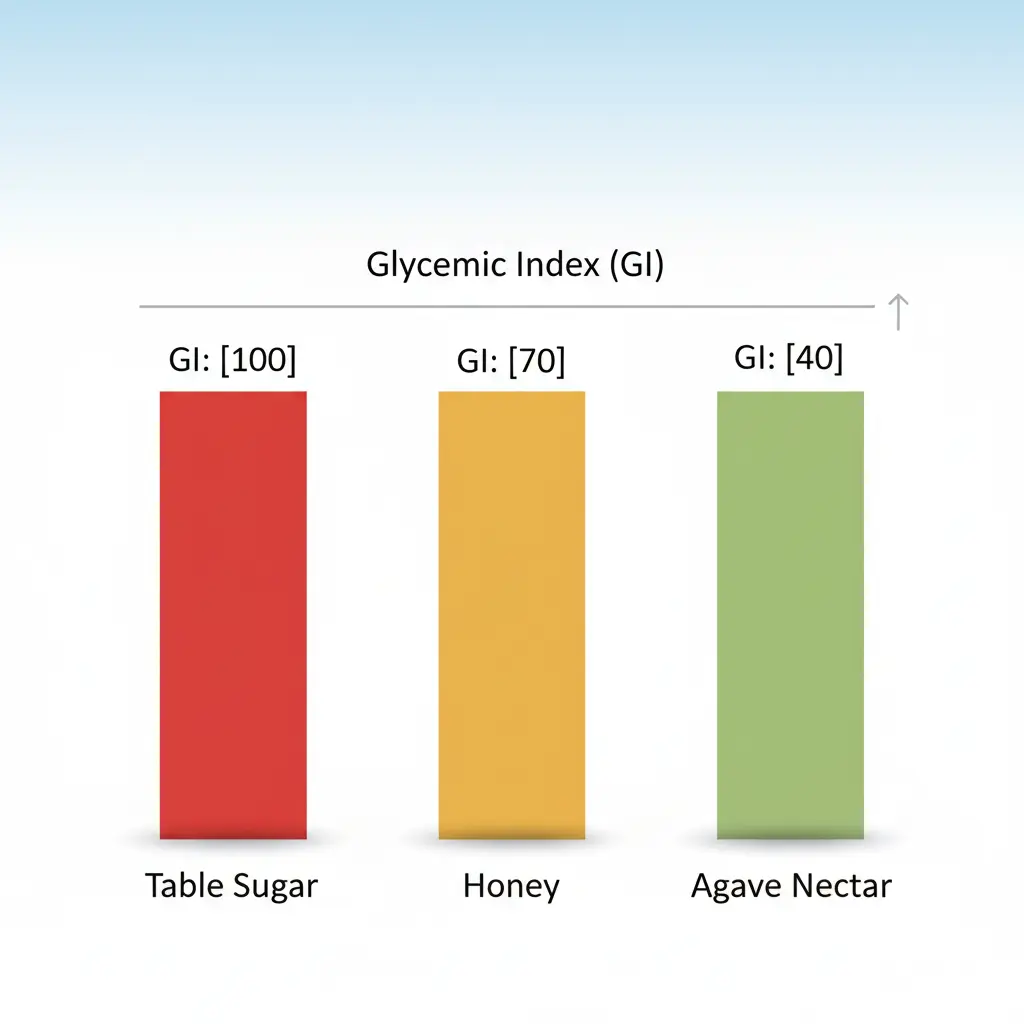
Honey does have a slightly lower glycemic index than refined sugar, which means it may raise blood sugar a little more slowly. However, the difference is small and does not make honey a free or safe food for diabetics.
Dr. Moxit Shah advises that honey should always be counted as part of your total carbohydrate intake to avoid unexpected blood sugar spikes.
How Does Honey Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
After consuming honey, the body digests it into simple sugars that enter the bloodstream. This leads to a rise in blood glucose levels. In people with diabetes, this increase can be stronger, especially if blood sugar is not well controlled.
Important points to understand:
• Honey has a moderate glycemic index but still increases blood sugar
• All sugars, including honey, count as carbohydrates
• Small amounts may raise blood sugar more slowly than sugar, but the rise still happens
Because honey is sweeter than sugar, some people use smaller quantities to achieve the same taste. While this may help reduce total carbohydrate intake, portion control remains essential.
Benefits and Risks of Eating Honey for Diabetics
Possible Benefits
Honey contains natural compounds that refined sugar does not provide. These include antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties that support overall health. Honey also has a slightly lower glycemic index compared to white sugar.
However, the health benefits are limited because honey is usually consumed in small amounts. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains offer better nutrition with less impact on blood sugar levels.
Risks and Considerations
Despite being natural, honey still poses risks for people with diabetes. It can cause blood sugar spikes if consumed in large quantities. Honey must be included in daily carbohydrate counting. Some commercially available honey products may also contain added sugars.
For these reasons, Dr Moxit Shah recommends consulting a healthcare provider before adding honey to a diabetes meal plan.

How to Include Honey Safely in a Diabetic Diet
If your doctor allows honey in your diet, follow these safe practices.
Use Very Small Amounts
A teaspoon of honey instead of a tablespoon can significantly reduce sugar intake. Always measure portions carefully.
Combine Honey with Fibre and Protein
Eating honey with fibre-rich or protein-rich foods such as plain yoghurt, nuts, or whole grains can slow glucose absorption and reduce blood sugar spikes.
Choose Pure and Natural Honey
Select raw and unprocessed honey that does not contain added sugars or syrups.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Check blood glucose before and after consuming honey. Individual responses can vary, and monitoring helps you understand how your body reacts.
Conclusion: Can Diabetics Eat Honey?
So, can diabetics eat honey? Yes, but only in moderation and with proper monitoring. Honey is not a sugar substitute that can be eaten freely.
Honey still raises blood sugar levels
It contains carbohydrates that must be counted
Small amounts may be acceptable when diabetes is well controlled
Always follow your personalised diabetes management plan and consult your healthcare provider before making dietary changes. When used carefully, honey can occasionally fit into a balanced diabetic diet without harming blood sugar control.
If you are unsure whether honey is safe for you, consult Dr Moxit Shah for personalised diabetes guidance and dietary advice tailored to your health needs. Early expert consultation can help you manage blood sugar more effectively and confidently.
FAQs
Can diabetics eat honey every day?
People with diabetes should not eat honey every day. Honey contains natural sugars that raise blood glucose levels. It may be consumed occasionally in small amounts if blood sugar is well controlled and approved by a doctor.
Is honey better than sugar for diabetics?
Honey has a slightly lower glycemic index than white sugar, but it still increases blood sugar levels. It is not significantly safer than sugar and should be treated the same way in a diabetic diet.
How much honey can a diabetic eat?
Most diabetics should limit honey to very small portions such as one teaspoon at a time. The exact amount depends on individual blood sugar control and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Does raw honey spike blood sugar?
Yes, raw honey can still spike blood sugar levels. Although it is natural and unprocessed, it contains glucose and fructose which raise blood sugar when consumed.
Can diabetics eat honey with other foods?
Honey is better tolerated when eaten with fibre or protein rich foods like yoghurt, nuts, or whole grains. These combinations slow glucose absorption and help reduce sudden blood sugar spikes.
Should diabetics consult a doctor before eating honey?
Yes, diabetics should always consult their doctor or dietitian before adding honey to their diet. Individual health conditions, medications, and glucose levels should guide this decision.